CBSE Class 6 Science – Curiosity – Takshila-DPS Pune- Patna-Coimbatore
AUTHOR
MBBS, DNB (DVL)
Dermatologist, Cosmetologist and Laser Surgeon
Nuleaf Skin Clinic and Hair Transplant Center, Undri, Pune
As a mother of twin daughters and a Consultant Dermatologist based in Undri, Pune, life is always a balancing act. Between busy clinic hours, parenting duties, and everyday chaos, I’ve been creating study notes since Class 4 to help my girls understand and revise their lessons better. Over the years, these weekend study sessions turned into a special tradition—discussing topics taught in school and turning them into organized, easy-to-revise notes.
The notes I’m sharing here are from the 2024–25 academic year of DPS Pune – Patna – Coimbatore, and cover Class 6 chapters. They include all the key points that are likely to be asked in exams, compiled from the Class 6 Curiosity textbook, school study materials, class notes and school revision sheets.
Each page was made with care, love, and a hope to make learning feel a little easier—especially during exam time. If they help your child too, then this effort finds even more meaning.
If you find these notes useful, I’d love to hear from you in the comments section. And if you’d like me to upload notes on any particular topic from Class 6, feel free to send in your suggestions.
Don’t forget to subscribe to my blog for new updates, notes, and posts.Wishing you and your child a wonderful academic year ahead!
Warmly,
Gauri
Mom to twins | raisingtwinsblog.in
IMPORTANT POINTS
- Temperature in Kelvin scale = Temperature in Celsius Scale + 273.15
- Range of human body temperature:
- Celsius scale – 35°C to 42°C
- Fahrenheit scale – 94 °F to 108 °F
- The SI unit for temperature is Kelvin
History of Thermometers:
- GALILEO GALILEI
Galileo Galilei invented a rudimentary water thermometer in 1593 which, for the first time, allowed temperature variations to be measured.
- DANIEL GABRIEL FAHRENHEIT
- In 1714, Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit invented the first mercury thermometer, the modern thermometer.
- In 1714 Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit is known as the Father of Thermometer because he invented the first reliable mercury thermometer, a reliable way to consistently tell the temperature.
- He was a German scientist born in the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth in 1686.
- All three temperature scales, Celsius, Fahrenheit, and Kelvin are named in honour of the scientists who developed these scales.
- ANDERS CELSIUS
- The degree Celsius is named after Anders Celcius, who invented the Celsius temperature scale.
- In the middle of the 18th century, Anders Celsius was professor of astronomy at the University of Uppsala, in Sweden.
- WILLIAM LORD KELVIN
- British physicist William Lord Kelvin became interested in the idea of “infinite cold” and made attempts to calculate it.
- In 1848 he published a paper, On an Absolute Thermometric Scale that stated that this absolute zero was, in fact, -273.15 degrees Celsius
NOTES
TEMPRATURE AND HEAT
Temperature (Defn): A reliable measure of the degree of hotness (or coldness) of a body is called its temperature.
Heat (Defn): Heat is a form of energy. It makes a substance hotter. If a body receives heat, its temperature rises and if a body loses heat, its temperature decreases.
Effect of Heat on Temperature:
- The temperature of a body increases on heating and decreases on cooling.
- We, therefore, often say that heat is the cause and temperature its effect.
- Substances expand on heating and contract on cooling.
Q) How can we tell if a body is hotter as compared to another body?
Ans) A hotter body has a higher temperature than a colder body. The difference in temperature between the two bodies tells us how hot a body is in comparison to another body.
THERMOMETERS
Thermometer (Defn): A device that measures temperature is called a thermometer.
Types of thermometer:
There are two kinds of thermometers that you are likely to come across—
- Clinical thermometers (Defn): A thermometer which is used for measuring body temperature is called a clinical thermometer. The range of a clinical thermometer is 35 °C-42 °C or 94 ºF-108 °F.
Examples:
- Clinical/ Mercury Thermometer
- Digital clinical thermometer
- Infra-red Thermometer
- Laboratory thermometers (Defn): A thermometer which is designed to measure the temperatures of objects, such as their boiling and melting points, in laboratories with high accuracy is called a laboratory thermometer. It is not designed to measure human body temperature. The range of a Laboratory thermometer is -10 °C to 110 °C.
- Maximum Minimum Thermometer.
CLINICAL THERMOMETER
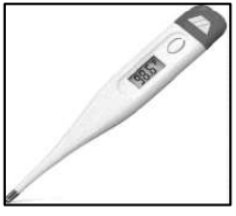
- DIGITAL CLINICAL THERMOMETER
- (Defn): A thermometer which is used for measuring body temperature and show temperatures digitally is called a Digital clinical thermometer.
- They run on batteries.
- Temperature in a digital thermometer is determined with the help of heat sensors.
- In digital thermometer, reading of temperature is displayed digitally as in digital watches.
- These measure temperature when the thermometer is placed in contact with a persons’ body.
- This is safer device as no mercury is used. Mercury is a highly toxic substance.
- For measuring temperature, the clinical thermometers generally use a scale called the Celsius scale. On this scale, the unit of temperature is degree Celsius and is denoted by °C.
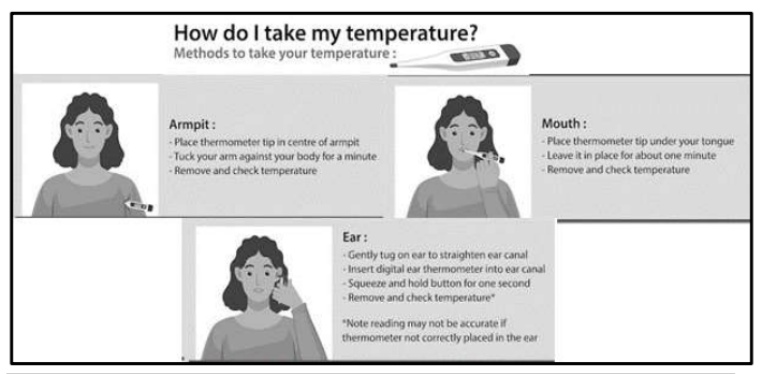
Q) How to measure body temperature?
- Wash your hands and the tip of the digital thermometer with soap and water.
- Reset the thermometer by pressing the reset button.
- Place the thermometer under the tongue and close your mouth.
- For measuring the body temperature of small children or old people, the digital thermometer can also be placed in the armpit.
- Wait till the thermometer makes a beeping sound or flashes a light.
- Take it out from the mouth and read the temperature on the digital display.
- Clean the tip of the thermometer with soap and water, and dry it.
Precautions to be taken while using a digital clinical thermometer:
- To be used after reading the instruction manual of the thermometer.
- Tip of the thermometer to be washed with soap and water before and after use.
- While washing, care to be taken to keep the digital portion such as the display out of water.
- Do not hold the thermometer by the tip.
- MERCURY THERMOMETERS:
Q) Why mercury thermometers are being replaced by digital thermometers.
Ans)
- Earlier, mercury thermometers were used for measuring the body temperature. But mercury is an extremely toxic substance and is difficult to dispose of if the thermometer breaks accidently.
- Digital thermometers use heat sensors and pose no such risk and also the numbers in its display are easier to read.
Therefore, mercury thermometers are being replaced by digital thermometers.
- There is a kink make near the bulb of clinical thermometer which prevents the automatic fall of mercury level.
Q) How to measure temperature using a clinical thermometer?
Ans)
- Take a clinical thermometer and hold it horizontally.
- Do not hold the thermometer from the bulb.
- Observe a shiny thin silvery thread i.e. mercury inside the tube.
- The end of the silvery thread shows the reading of temperature. If mercury lining ends at 37, the reading is 37°C.
- Wash the bulb end of thermometer with an antiseptic solution.
- Give two or three jerks slightly. By doing this the mercury level would fall.
- When it falls to 35°C or below, put it below the tongue and wait for one minute.
- Take out the thermometer and read the temperature.
- The normal body temperature is 37°C. This can differ from person to person.
Q) What are the precautions to be taken while using a clinical thermometer?
Ans) Precautions to be taken while reading temperature using a clinical thermometer:-
- Wash the thermometer before and after every use with an antiseptic lotion.
- Handle it with care. If it hits against some hard object, it can break because it is a very delicate thing.
- See that the mercury levels are below 35 degrees and do not hold the thermometer near its bulb while reading the temperature.
- While noting down the temperature from the thermometer, place the mercury level along the line of eye sight.
- Do not place the thermometer near a hot flame and also do not expose it to the direct sun light.
- Give a gentle jerk to the thermometer before checking the temperature levels, so that the mercury comes back to its initial point i.e. where it had been before the temperature was taken.
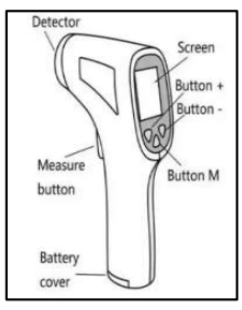
- INFRARED THERMOMETERS
- It is a non-contact thermometer or temperature guns.
- It infers temperature from a portion of the thermal radiation emitted by the object being measured.
- They are sometimes called laser thermometers as a laser is used to help aim the thermometer, to describe the device’s ability to measure temperature from a distance.
- Infrared thermometers are non-contact thermometers and can measure temperature without touching a person’s body and thus reduce the risk of spreading disease.
- They were used widely during the COVID-19 pandemic since they could measure the temperature of a person from a distance and maintain social distancing.
Normal body temperature:
- The normal temperature of a healthy human body is taken to be 37.0 °C.
- Normal temperature is the average body temperature of a large number of healthy people. Hence, the temperature of every person may not be 37.0 °C.
- The body temperature is influenced by several factors, such as age, time of the day and activity level.
- The temperature of human beings does not normally go below 35 °C or above 42 °C.
- The temperature measured when the thermometer is kept in the armpit is about 0.5 °C to 1 °C lower than the actual body temperature. (children and old people)
- Small children tend to have slightly higher body temperatures compared to adult due to their faster metabolic rate. Healthy older adults often have lower body temperatures because as people age, their bodies tend to have a slower metabolic rate.
Temperature Scales:
Fahrenheit scale:
- On this scale, the unit of temperature is degree Fahrenheit and is denoted by °F.
- A temperature measured as 37.0 °C on Celsius scale is equivalent to 98.6°F on Fahrenheit scale.
- The Fahrenheit scale is not used in most scientific studies anymore.
Kelvin scale:
- In scientific work, there is another scale of temperature known as Kelvin scale.
- On this scale, the unit for temperature is kelvin and is denoted by K.
- The SI unit of temperature is kelvin.
- All three temperature scales, Celsius, Fahrenheit and Kelvin are named in honour of the scientists who developed these scales.
- We can easily convert the temperature from Celsius scale to Kelvin scale by using: Temperature in Kelvin scale = Temperature in Celsius scale + 273.15
To read only:
- The names of temperature scales—Celsius scale, Fahrenheit scale and Kelvin scale—start with a capital letter.
- For the units for temperature, degree Celsius and degree Fahrenheit, the word degree starts with a lower-case letter while Celsius and Fahrenheit start with a capital letter.
- The unit kelvin starts with a lower-case letter.
- The symbols of all units (°C, °F, K) are capital letters.
- Note that degree sign (°) is not written with K.
- A full stop is not written after the symbol, except at the end of a sentence.
- While writing the temperature, a space is left between the number and the unit.
- For temperatures more than one degree, use the plural of ‘degree’, that is, ‘degrees’, while writing the full form of the unit.
Q) How was fever detected before thermometers were developed?
Ans) Fever affects the pulse rate of a person. This was known even in olden days in India. However, apart from fever, some other situations also affect the pulse rate. Hence, pulse rate alone is not a reliable indicator of fever.
Q) Can a clinical thermometer be used for measuring the temperature of boiling water? Or for measuring the temperature of ice?
Ans) No, the temperatures of boiling water and ice are outside the range of a clinical thermometer. It requires Laboratory thermometer.
- A perfectly healthy person may, have a normal temperature slightly different from 37.0 °C. Why?
Ans) Normal temperature is the average body temperature of a large number of healthy people. Hence, the temperature of every person may not be 37 °C.
LABORATORY THERMOMETER
- It consists of a long, narrow, uniform glass tube which is sealed.
- At one end of the tube is a bulb which contains a liquid.
- Outside the bulb, in the tube, a narrow column of liquid can be seen.
- The liquid used in the laboratory thermometer is generally alcohol (coloured red to make it easily seen) or mercury
- The liquid column rises or falls with change in temperature.
- There is a Celsius scale marked along the tube.
- The mark of the Celsius scale with which the top level of the liquid column coincides is the temperature reading.
- The scale of temperature is graduated generally from 10°C to 110°C
- The temperature difference indicated between 0 °C and 10 °C or between 10 °C and 20 °C is 10 °C. Hence, each division of temperature scale is further divided into 10 parts to read fraction of temperature
- So, one small division can read 10/10 = 1 °C. That is, the smallest value that this thermometer can read is 1 °C.
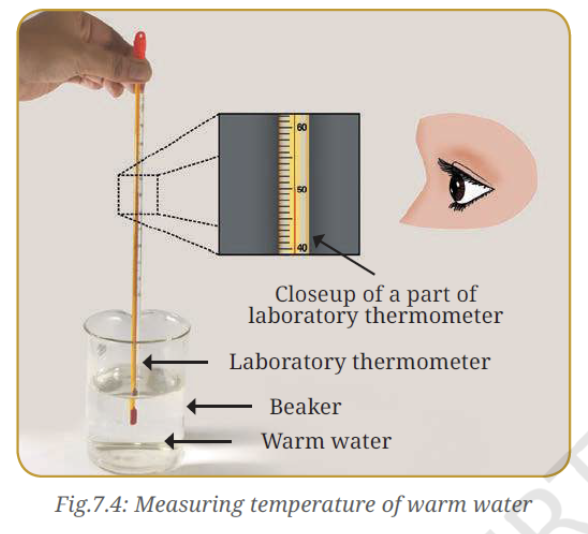
Correct way of measuring temperature using a laboratory thermometer:
- The bulb of the thermometer should dip well in the liquid.
- When the thermometer is immersed in water, its bulb should not touch the bottom or the sides of the beaker.
- The thermometer should be held vertically. It should not be tilted.
- The temperature must be read while the thermometer is immersed in water.
- Read the upper meniscus.
- While reading the thermometer, the eye should be directly in line with the level of the liquid column to be read.
Precautions to be taken while using a laboratory thermometer:
• Handle with care. If it hits against some hard object, it can break.
• Do not hold it by the bulb.
Let us measure:
- Take some warm water in a beaker.
- Dip the thermometer in water so that the bulb is immersed in water
- Observe the rise of liquid column in the thermometer.
- Wait till the column stops rising and note the temperature (do not wait too long; otherwise, the water itself will start to cool).
- As soon as you take the thermometer out of the water, the level of liquid
Column begins to fall? This means that the temperature must be read while the thermometer is immersed in water.
- You may have noticed that the temperature of water remains constant while it is boiling. Also, the temperature of ice remains constant while it is melting
AIR TEMPERATURE
Maximum-Minimum Thermometer (Defn): It is used to measure the daily temperature to prepare weather reports.
Room Thermometer (Defn): Room thermometer gives an approximate idea of the room. It is hung on walls of your school laboratory, doctor’s clinic, and hospitals.
Because weather depends on several factors, these temperatures usually vary every day. Generally, as we approach the summer season, the temperature rises and during the winter season it falls.
There are many techniques for measuring air temperature. Air temperature is an important weather parameter and is monitored at weather stations all over the world. The data gathered on air temperature along with various other parameters are used for making weather forecasts.
Anna Mani:
- Anna Mani (1918–2001) was an Indian scientist, also known as the ‘Weather Woman of India’.
- She invented and built a large number of weather measurement instruments.
- This reduced the reliance of India on other nations for such instruments.
- She also explored the possibilities of using wind and solar energy in India.
- Her work helped India to become one of the global leaders in renewable energy.
QUESTION AND ANSWERS:
Q.1) On measuring the body temperature, Anna saw that her body temperature was 98.6°F. Do you think she is suffering from fever?
Ans) Average body temperature is 98.4°F, But our body temperature may vary due to age, time of the day and activity level. Hence Anna is not sick.
Q.2) Do you think a clinical thermometer can measure the temperature of boiling water or ice? Give reasons to support your answer.
Ans) The range of a clinical thermometer is 35°C-42°C or 94ºF-108°F. It cannot measure the temperature of ice (0ºC) or boiling water (100ºC) as they don’t fall in this range.
Q.3) Convert 37ºC into Kelvin
Ans) 37ºC + 270 = 307ºC
Q.4) How was fever detected in the olden days before thermometer were developed?
Ans) Fever affects the pulse rate of a person. Hence if the pulse varied much higher than usual then the person was having fever.
Q.5) List four precautions that need to be taken while using a digital thermometer.
Ans)
- To be used after reading the instruction manual of the thermometer.
- Tip of the thermometer to be washed with soap and water before and after use.
- While washing, care to be taken to keep the digital portion such as the display out of water.
- Do not hold the thermometer by the tip
Q.6) Similarities between between a clinical and a laboratory thermometer
Ans)
- Both consist of a long narrow glass tube.
- Both of them have a bulb at one end.
- The bulbs of both consist of mercury.
- Both thermometers contain a Celsius scale.
Q.7) Give 2 points of difference between a clinical and a laboratory thermometer
Ans)
| Clinical Thermometer | Laboratory Thermometer | ||
| 1 | A thermometer which is used for measuring body temperature is called a clinical thermometer | 1 | A thermometer which is designed to measure the temperatures of objects, such as their boiling and melting points, in laboratories with high accuracy is called a laboratory thermometer |
| 2 | The range of a clinical thermometer is 35 °C-42 °C or 94 ºF-108 °F. | 2 | The range of a Laboratory thermometer is -10 °C to 110 °C |
| 3 | Graduated in both Fahrenheit and Celsius | 3 | Graduated in Celsius |
| 4 | Mercury level does not fall on its own as there is a kink near the bulb to prevent the fall of mercury level. | 4 | Mercury level falls on its own as there is no kink present |
| 5 | Jerk is given to lower the mercury level | 5 | No jerk is given to lower the mercury level. |
| 6 | Temperature can be read after removing it | 6 | Temperature is read while being in contact with it |
Q.8) What is the correct way of measuring temperature using a laboratory thermometer?
Ans)
- When the thermometer is immersed in water, its bulb should not touch the bottom .8 the sides of the beaker.
- The thermometer should be held vertically. It should not be tilted.
- The temperature must be read while the thermometer is immersed in water.
- While reading the thermometer, the eye should be directly in line with the level of the liquid column to be read.
Q.9) Small children have higher body temperatures as compared to old people. How? Justify your answer with one point.
Ans) Small children tend to have slightly higher body temperatures compared to adult due to their faster metabolic rate. Healthy older adults often have lower body temperatures because as people age, their bodies tend to have a slower metabolic rate.
Q.10) Why are digital clinical thermometers preferred over mercury clinical thermometer?
Ans) Earlier, mercury thermometers were used for measuring the body temperature. But mercury is an extremely toxic substance and is difficult to dispose of if the thermometer breaks accidently. Digital thermometers use heat sensors and pose no such risk and also the numbers in its display are easier to read.
Thanks a lot for visiting my blog. Please do ‘★ LIKE’ the post if you found it to be useful. Your comments, suggestions, criticism and all opinions are very much appreciated. Please do write your queries in the Reply/comments section and I will try to get back to you asap.

All the content on this blog is copyrighted. It takes immense research, hard work, patience and time to come up with a comprehensive article/post. If you like and need to use any of my article(s) or any part of it, please do give the requisite reference, link or credit to my website/blog . DO NOT COPY WITHOUT PERMISSION.