CBSE Class 6 Science – Curiosity – Takshila-DPS Pune- Patna-Coimbatore
AUTHOR
MBBS, DNB (DVL)
Dermatologist, Cosmetologist and Laser Surgeon
Nuleaf Skin Clinic and Hair Transplant Center, Undri, Pune
As a mother of twin daughters and a Consultant Dermatologist based in Undri, Pune, life is always a balancing act. Between busy clinic hours, parenting duties, and everyday chaos, I’ve been creating study notes since Class 4 to help my girls understand and revise their lessons better. Over the years, these weekend study sessions turned into a special tradition—discussing topics taught in school and turning them into organized, easy-to-revise notes.
The notes I’m sharing here are from the 2024–25 academic year of DPS Pune – Patna – Coimbatore, and cover Class 6 chapters. They include all the key points that are likely to be asked in exams, compiled from the Class 6 Curiosity textbook, school study materials, class notes and school revision sheets.
Each page was made with care, love, and a hope to make learning feel a little easier—especially during exam time. If they help your child too, then this effort finds even more meaning.
If you find these notes useful, I’d love to hear from you in the comments section. And if you’d like me to upload notes on any particular topic from Class 6, feel free to send in your suggestions.
Don’t forget to subscribe to my blog for new updates, notes, and posts.Wishing you and your child a wonderful academic year ahead!
Warmly,
Gauri
Mom to twins | raisingtwinsblog.in
IMPORTANT POINTS
- There are many types of carbohydrates. The main carbohydrates found in our food are in the form of starch and sugars.
- Foods containing fats and carbohydrates are also called ‘energy giving foods.
- Fats give much more energy as compared to the same amount of carbohydrates.
- Proteins are needed for the growth and repair of our body.
- Foods proteins are often called ‘body building foods’.
- One can eat a balanced diet without expensive food materials.
- We all know that cooking improves the taste of food and makes it easier to digest. At the same time, cooking also results in the loss of certain nutrients.
- The major nutrients in our food are carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins and minerals. In addition, food also contains dietary fibres and water.
- Carbohydrates and fats mainly provide energy to our body.
- Proteins and minerals are needed for the growth and the maintenance of our body.
- Vitamins help in protecting our body against diseases.
- Balanced diet provides all the nutrients that our body needs, in right quantities, along with adequate amount of roughage and water.
- Deficiency of one or more nutrients in our food for a long time may cause certain diseases or disorders.
- The main components of foods like carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, minerals, fibres and water are required by our body in adequate amount for proper functioning. These are called nutrients.
- Some nutrients get lost in the process of cooking and preparations. For example boiling for a long time or too much cooking and lead to loss of vitamin B & C.
- If the vegetables and fruits are washed after cutting or peeling them, it may result in the loss of some vitamins. The skins of many vegetables and fruits contain vitamins and minerals.
- Similarly, repeated washing of rice and pulses may remove some vitamins and minerals present in them.
- Many useful proteins and considerable amounts of minerals are lost if excess water is used during cooking and is then thrown away.
- Peeling before boiling increases the loss of Vitamins.
- Vit D helps our body to use calcium for bones and teeth.
- Edible mushrooms are good sources of protein.
NOTES
Food in different regions:
- Diversity in food exists in all states
- Traditional food of any state is usually based on the crops grown in that state
- Various crops are grown in different regions depending on the types of soil and climatic conditions.
- Choice of food may vary on the food crop cultivated, taste preferences, culture and traditions.
- Culinary practices have changed over time, from traditional to modern ways of cooking. E.g Gas stoves have replaced chulhas and electric grinder has replaced Sil-batta (Stone grinder).
TO READ:

Components of food
Nutrition (Defn): The various modes of consuming food and its utilization in the body of living organism for energy, growth and repair is called nutrition.
Nutrient (Defn): A nutrient is a substance used by an organism to survive, grow, and reproduce. Our food contains six main nutrients.
Nutrients Food contains different nutrients that can be grouped into three categories based on their utility in the body:
- Energy giving Food: carbohydrates & fats
- Body building Food: proteins
- Protective Food: minerals and vitamins
CARBOHYDRATES: (Energy giving food)
- It is made up of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen.
- Uses: Carbohydrates give us energy to do work and are called energy giving nutrients.
- Types: There are three types of carbohydrates:
- Sugars:
- It is a simple carbohydrate having sweet taste.
- Sources of sugar are glucose, Sugarcane, milk and fruits such as banana, apple, grapes, etc.
- Starch:
- It is a complex carbohydrate. It is a tasteless, colourless, white powder.
- Sources of starch are Wheat, maize, potato and rice.
- Cellulose:
- It is a complex carbohydrate.
- It is present in plant cell wall.
- Humans cannot digest cellulose.
PROTEINS (Body building food)
- Soya beans contain maximum proteins.
Uses:
- Proteins are body building nutrients.
- Proteins are required for proper growth and repair of our body.
- Proteins are needed for proper growth of bones, muscles, skin, nail and hair.
Requirement:
- The daily requirement of protein for adults is 1 gram per kilogram of the body weight.
- When the body is building new tissues, more proteins are required, so growing children and pregnant ladies need more protein.
FATS (Energy giving food)
- Fats are made up of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen.
- An adult need about 35 g fat every day.
- Uses:
- Fats are essential for the absorption of vitamins A, D, E and K in the body
- Stored energy: Our body stores the excess energy in the form of fat. The stored fat is used by our body for producing energy as and when required so fat is considered as energy bank in our body.
- Fat in our body also prevents heat loss from the body surface, i.e., insulating.
- Fats give more energy than carbohydrates.
- Obesity:
- Excess of fat is stored in our body under the skin.
- If we are physically active and need more energy, fats could serve as useful source of energy. But, if we are physically inactive, too much fat in our diet can lead to obesity (overweight).
- Obesity causes heart problems.
VITAMINS: PROTECTIVE NUTRIENTS
- Vitamins are required in small quantity by our body regularly.
- Types: Based on their solubility, vitamins are grouped into two classes:
- Water soluble Vitamins: Vitamin C and Vitamin B complex
- Fat soluble Vitamins: Vitamin A, D, E and K.
- Sources:
- Vitamins cannot be made by our body so; we need to take them through our food.
- Fresh fruits and vegetables are rich sources of vitamins.
- However, our skin can make vitamin D in the presence of sunlight.
- Uses:
- This nutrient keeps our body safe from diseases. These are called protective nutrients.
- They perform specific functions in our body. For example, certain chemical reactions in our body will not take place if vitamins are not present.
- Vitamins also help in keeping our eyes, bones, teeth and gums healthy.
| Vitamins | Functions |
| Vitamin A | Keeps our skin and eyes healthy. |
| Vitamin C | Helps body to fight against many diseases. |
| Vitamin D | Helps our body to use calcium for bones and teeth. |
MINERALS
- Minerals are needed by our body in small amounts.
- Minerals: iron, calcium, phosphorus, iodine, sodium, potassium, zinc, copper etc.
- Uses:
- Each one is essential for proper growth of body and to maintain good health.
- Deficiency of minerals in our body causes various diseases.
- Some minerals help to build strong bones and healthy teeth. (calcium)
| Mineral | Source | Function | Deficiency symptoms |
| Calcium | Milk, eggs, cheese | Formation of strong bones & teethMuscle contractionBlood clotting | Brittle bones and tooth decayPoor muscle movementExcessive bleeding |
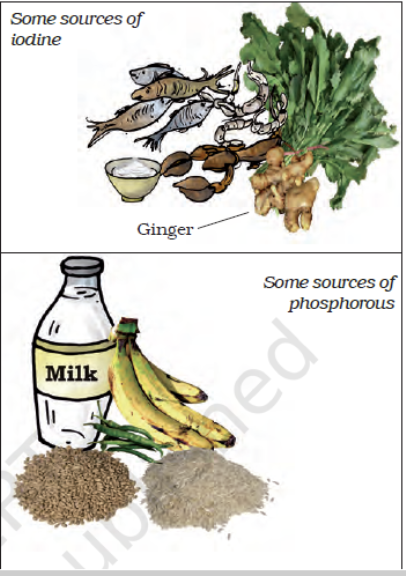
| Phosphorus | Bananas, milk, egg | Formation of strong bones and teeth. | Body weakness, weak bones and teeth |
| Iron | Green leafy vegetables, liver, jaggery | Formation of haemoglobin (oxygen carrying pigment in RBC) | Anaemia (lack of haemoglobin) |
| Iodine | Salt, ginger, dried fish (sea food) | Proper functioning of thyroid gland | Goitre (swelling of thyroid gland) |
DIETARY FIBRES / ROUGHAGE
- Definition: The fibrous indigestible plant cellulose material mainly provided by plant products in our food that helps to get rid of undigested food from the digestive system is called Roughage
- Uses:
- It helps in preventing constipation and makes our digestion smooth and easy.
- It adds bulk to the food and gives a sense of fullness after the meal.
- Sources: Salad, vegetables, sprouted grains and fruits are the sources of roughages.
- Roughage does not provide any nutrient to our body.
WATER
- Water forms about 70% of our body weight and is an important constituent of all body cells.
- We must drink at least 8 glasses of water a day.
- It is an important component of our nutrition.
- Functions:
- Helps in digestion by dissolving nutrients, which can then be absorbed or digested by the body.
- Transports food, wastes, gases and other chemicals (hormones) throughout the body.
- It carries waste out of the body in the form of sweat and urine.
- Helps to regulate body temperature
- Sources:
- We get most of the water that our body needs from the liquids we drink — such as water, milk and tea.
- In addition, we add water to most cooked foods.
- Some vegetables and fruits also contain water.
Sources of food
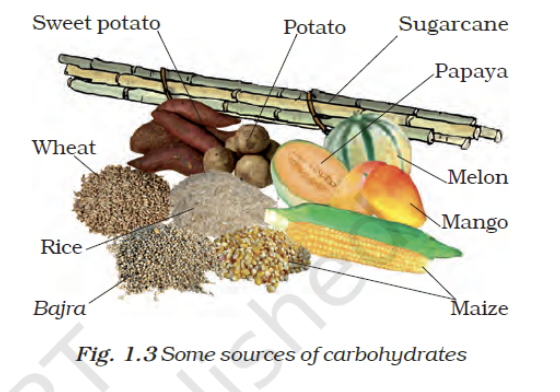
- Carbohydrate –
- Starch: Sweet potato, potato, wheat, rice, bajra, maize
- Sugar: papaya, melon, mango, banana, sugarcane
- Fats –
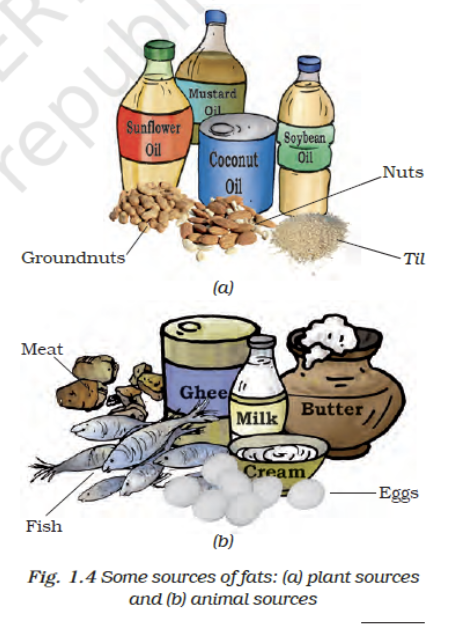
- Plant sources – Sunflower oil, mustard oil, coconut oil, soyabean oil, nuts, groundnuts, til.
- Animal sources – Meat, fish, eggs, milk, butter, ghee.
- Proteins
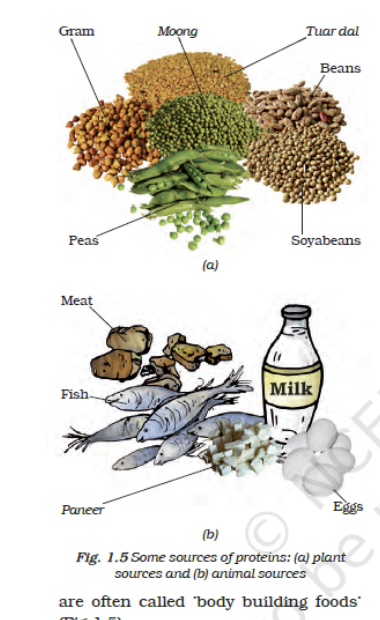
- Plant sources – Gram, moong, Toor dal, beans, soyabeans, peas.
- Animal sources – Meat, fish, eggs, milk, paneer.
- Vitamins
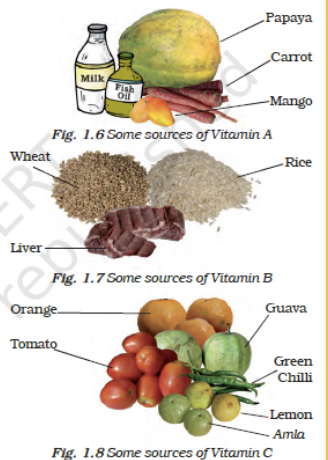
- Vitamin A –Papaya, Carrot, Mango
- Vitamin B – Wheat, rice, liver
- Vitamin C – Orange, tomato, guava, green chilli, lemon, amla
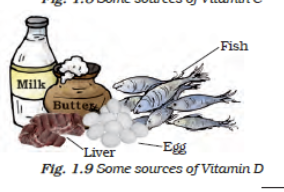
- Vitamin D – Fish, liver, egg
- Minerals
- Iodine – salt, ginger, dried fish
- Phosphorous – bananas, milk
- Iron – green leafy vegetables, liver, jiggery, apples
- Calcium – milk, eggs
Tests for nutrients in food
| Nutrient | Test | Result |
| Test for starch | Take a small quantity of a food item or a raw ingredient. Put 2-3 drops of dilute iodine solution on it. | A blue-black colour indicates that it contains starch. |
| Test for Protein | Take a small quantity of a food item for testing. Grind (into paste/powder) or mash a small quantity of the food item. Put some of this in a clean test tube, add 10 drops of water to it and shake the test tube. Now, using a dropper, add two drops of solution of copper sulphate and ten drops of solution of caustic soda to the test tube. Shake well and let the test tube stand for a few minutes. | A violet colour indicates presence of proteins in the food item. |
| Test for Fats* | Take a small quantity of a food item. Wrap it in a piece of paper and crush it.Take care that the paper does not tear.Now, straighten the paper and observe it carefully. Does it have an oily patch?Hold the paper against light. Are you able to see the light faintly, through this patch? | An oily patch on paper shows that the food item contains fat. |
| Test for water | Take a tomato or a fruit like lemon. Cut it into small pieces. | If your hands get wet while doing so it contains water. |
*The food items may sometimes contain a little water. Therefore, after you have rubbed an item on paper, let the paper dry for a while. If there were any water that may have come from food, it would dry up after some time. If no oily patch shows up after this, the food item does not contain any fat.
| Dilute solution of iodine | Add few drops of tincture iodine to a test tube half filled with water |
| Copper sulphate solution | Dissolving 2gm of copper sulphate in 100 ml of water |
| Caustic soda solution | Dissolving 10gm of caustic soda in 100ml of water |
Balanced Diet
Diet (Defn): The food we normally eat in a day is our diet.
Balanced Diet (Defn): A diet that provides all the nutrients that our body needs, for its growth and maintenance in the proper amount is called a balanced diet. The diet should also contain a good amount of roughage and water.
Deficiency diseases
Deficiency Diseases (Defn): Diseases that occur due to lack of nutrients over a long period are called deficiency diseases. It can be cured on taking a balanced diet.
| Vitamins/Minerals/ Carbohydrates/ Proteins | Deficiency disease/disorder | Symptoms |
| Proteins | Kwashiorkor | Stunted growth, Skin becomes dry and scalyBody swells up, Large pot like belly, Limbs become thin and bony |
| Carbohydrates and Proteins | Marasmus | Body becomes very lean and thin the child may not be able to moveRibs become prominentSunken eyesGrowth stops completely |
| Vitamin A | Night blindness | Unable to see in dim light.Poor visionSometimes complete loss of vision |
| Vitamins B1 | Beriberi | Weight lossVery less energy to workEmotional disturbancesWeakness and pain in limbs Irregular heart rateSwelling of body. |
| Vitamin B2 | Pellagra | Redness of tongue, DiarrhoeaSkin eczema, Mental confusion. |
| Vitamin C | Scurvy | Bleeding gums, Loosening of teethLate healing of wounds. |
| Vitamin D | Rickets | Softening of bones, Bending the bones (knock knees) Dental problems |
| Iodine | Goitre | Glands in the neck appear swollenMental disability in children |
| Iron | Anaemia | Weakness, Paleness of nails and face. |
Malnutrition:
Malnutrition (Defn): Malnutrition is a serious condition that occurs when the body doesn’t have the right amount of nutrients to maintain healthy tissues and organ function.
| Kwashiorkor | Marasmus | |
| Causes | Deficiency of proteins. | Deficiency of both proteins and calories. |
| Symptoms | Accumulation of water results in edema. Weight loss | No edema is observed. Severe weight loss |
Junk Food (Defn): Food which have high calories due to high sugar and fat content and contain very low amounts of proteins, minerals, vitamins and dietary fibres are called junk food. It makes people obese and suffers from several health problems.
MILLETS: Nutrition rich cereals
- (Defn): Millets are small size grains and known as nutria-cereals as they provide most of the nutrients required for the normal functioning of our bodies .They have been part of Indian diet for centuries.
- Jowar, bajra, ragi and sanwa are the native crops of India. Their grains are highly nutritious and are called millets.
- They are good sources of vitamins, minerals like iron and calcium and dietary fibres
- They can be easily cultivated in different climatic conditions.
Food miles:
- Food miles (Defn): The entire distance travelled by a food item, from the producer to the consumer is known as food miles.
- Reducing food miles are important because it helps to cut down the cost and
pollution during its transport supports local farmers and also keeps our food fresher and healthier.
- We must aim to reduce food miles.
Question and answers:
Q.1) In what ways are nutrients lost in food?
Ans)
Peels
- Boiling: Root vegetables should be boiled with skins on and then peeled after boiling. This helps the nutrients to migrate to the centre of the vegetables, helping better retention of its nutrients.
- Peeling: When peeling the skin of vegetables do peel as thinly as possible. The nutrients in vegetables and fruits are concentrated just below the skin,
- Do eat with skin on whenever possible.
Soaking, Washing & Boiling:
- Soaking: Do not soak vegetables in water to prevent discoloration. Almost 40 % of vitamins and minerals are lost in the soaking water. If you must soak, use up the soaking water to knead dough, prepare soups and gravies.
- Washing: Certain amount of minerals and vitamins are lost when washing grains before cooking. That’s why it is preferable to wash rice with minimum amount of water.
- Boiling: Do not throw away the excess water drained after boiling rice or vegetables.
Cutting:
Do not cut vegetables into very small cubes as each small part comes in contact with oxygen, destroying vitamins.
Milk and Cottage cheese:
- Milk: Do not keep milk open or exposed to light, as considerable destruction of riboflavin (Vitamin B2) can occur.
- Cottage cheese: When preparing cottage cheese, the water left over after curdling is called ‘whey’. It is extremely rich in good quality proteins and vitamins and should be used up in preparing gravies, kneading dough or simply had as a refreshing drink after flavouring with lemon juice and salt and pepper.
Reheating: Reheating cooked vegetables further destroys vitamins
Q.2) Why is it sensible to include some fruits and raw vegetables in our diet?
Ans) Vitamin C gets easily destroyed by heat during cooking, hence is it sensible to include some fruits and raw vegetables in our diet.
Q.3) Prepare a diet chart to provide balance diet to a twelve year old child. The diet chart should include food items which are not expensive and are commonly available in your area.
| Breakfast | Lunch | Dinner | |
| Monday | Egg omelette with wheat bread | Rice- dal – Vegetable | Rajma- Rice |
| Tuesday | Aloo parantha | Rice- egg curry | Chole- Rice |
| Wednesday | Methi Parantha | Chappati – matter paneer | Vegetable pulav |
| Thursday | Uppit | Curd rice | Rice- dal – Vegetable |
| Friday | Poha | Chicken curry | |
| Saturday | Poori bhajji | Vegetable Pulav | Dal Khichdi |
| Sunday | Idli – Vada | Chicken biryani | Chappati and bhajji |
Q.4) A katori (bowl) of fat will give much more energy than a katori of carbohydrate rich food. So, is it sensible to eat nothing but food rich in fats like samosa and poori (snacks), malai, rabdi and peda (sweets)?
Ans) No, of course not! It can be very harmful to eat too much of fat rich foods and we may end up suffering from a condition called obesity. Obesity causes heart problems.
Q.5) Why is rice called a ‘carbohydrate rich’ source of food?
Ans) In a given raw material, one particular nutrient may be present in much larger quantity than in others. For example, rice has more carbohydrates than other nutrients. Thus, we say that rice is a “carbohydrate rich” source of food.
Q.6) What is obesity?
Ans) Obesity is a medical condition characterized by excessive accumulation and storage of fat in the body, leading to a body mass index (BMI) of 30 or higher.
Q.7) Is a Balanced Diet the Same for Everyone?
Ans) No, a balanced diet is not the same for everyone and varies depending on n factors such as age, gender, occupation, health status, activity level etc.
For example:
- Children and pregnant women require more proteins compared to adults.
- Athletes and manual labourers require more carbohydrates and proteins compared to sedentary workers
Q.8) Why do Polar bears accumulate a lot of fat under their skin?
Ans) Polar bears accumulate a lot of fat under their skin. This fat serves as an energy source. It supports them during their months long winter sleep (hibernation), enabling them to survive without eating.
Deficiencies:
- Nutrition: The various modes of consuming food and its utilization in the body of living organism for energy, growth and repair is called nutrition.
- Nutrient: A nutrient is a substance used by an organism to survive, grow, and reproduce. Our food contains six main nutrients.
- Diet: The food we normally eat in a day is our diet.
- Balanced Diet: A diet that provides all the nutrients that our body needs, for its growth and maintenance in the proper amount is called a balanced diet. The diet should also contain a good amount of roughage and water.
- Malnutrition: Malnutrition is a serious condition that occurs when the body doesn’t have the right amount of nutrients to maintain healthy tissues and organ function.
- Deficiency Diseases: Diseases that occur due to lack of nutrients over a long period are called deficiency diseases.
- Millets: Small size nutritious cereal.
- Food miles: The distance travelled by a food item, from the place of production to the consumer
Thanks a lot for visiting my blog. Please do ‘★ LIKE’ the post if you found it to be useful. Your comments, suggestions, criticism and all opinions are very much appreciated. Please do write your queries in the Reply/comments section and I will try to get back to you asap.

All the content on this blog is copyrighted. It takes immense research, hard work, patience and time to come up with a comprehensive article/post. If you like and need to use any of my article(s) or any part of it, please do give the requisite reference, link or credit to my website/blog . DO NOT COPY WITHOUT PERMISSION.